Sunday, 21 August 2016
Wednesday, 17 August 2016
How to easily repair Momentary Switches used in boats
dvbot
05:53
Corroded Momentary switches, diy simple boat electrics, how to fix horn button, how to fix switches on boat, Momentary switches, simple boat switch fix
No comments
![]()
 |
| If your horn won't blow, or blows erratically, it's probably the switch that is causing the problem |
A momentary switch can come in various structures. You are presumably most acquainted with the little push button on your panel or board in charge. How about we take the button for horn for instance. You push it in and the horn blows. You take your finger off, it pops pull out, and the horn quits blowing. Assume the horn doesn't blow, or blows whimsically, when you push the button in. The issue might be eroded connections at the switch terminals or somewhere else. This is anything but difficult to fix so check connections at the switch, horn, and power sources, before going any further. On the off chance that you see erosion or different weaknesses, for example, a loose connection, settle that first. This might be as basic as fixing a screw or detaching the connection, cleaning it with a abrasive, including a squirt of moisture disbursing oil, and reassembling. In the event that you don't see an issue with the wiring and connection, suspect the switch.
Finding the root of problem
 |
| Momentary switch from a horn - the wires attach to the terminals at the base. |
 |
| Carefully opening switch by bending back tabs. |
 |
| Removing terminal plate from switch box. |
In deep working of the switch
Given how basic momentary switches are, what can turn out badly?Generally the contact points get to be hollowed or eroded to the degree that they pass either no current or current deficient to carry out the work well. The fix might be to just sand or file the contacts. You should disconnect the wiring and remove the switch from the panel board first and open the lodging at that end of the switch. This might be simple or not worth the exertion, depending upon the switch, but rather in a crisis circumstance you might be happy you know how to take care of the issue at least temporarily.
 |
| With the terminal plate removed and the switch depressed, you can see the two humps on the jumper bar at the base of the switch, which make contact with the contact pads on the terminal plate to close the circuit. |
 |
| In this switch, the contact pads have become corroded and pitted, and the jumper bar is askew. |
 |
| After partial filing and cleaning, most of the corrosion on the contact pads has been removed, but the depression on the left-hand pad from arcing may interfere with a good contact. |
Another sort of issue is that the contact part moves or becomes dislodged from its assembly and in this way doesn't solidly seat against the rear of the wire terminals when you push the button. This is normally brought on by age and wear, and is from time to time worth fixing. (A well-made switch will regularly keep going quite a while before this happens.)
A third issue can happen if there is obstacle between the plunger and the shaft walls in which it moves. This could happen from issues, for example, a lot of oil or lubricant that has solidified from dirt, or from corrosion. Contingent upon the build of your switch, this might be simple or hard to get to, and clean utilizing light emery polishing paper or maybe only a rough clean rag. It can be an especially troubling issue in light of the fact that frequently the plunger gets stuck in the down position, implying that the horn won't turn off. This issue is far more awful if the momentary switch is being utilized to begin the engine. It is common for these switches to stick down in this application, making the starter solenoid stay activated, and therefore keeping on running the starter even after the motor has fired off. This can rapidly ruin an extremely costly starter and related parts and is a justifiable reason to replace these moderately cheap switches frequently.
Wednesday, 30 December 2015
Simple 3 Watt and 5 Watt LED Driver Circuit Using IC 338
dvbot
08:35
12 volt battery led driver for 5 watt and 3 watt, car tail light led driver, led driver for vehicle like motorbike and car, led driver using lm338
1 comment
![]()
In the present outline, the gadget is designed in the programmed current control mode.
White LEDs particularly require a very much dimensioned info, actually the current to these LEDs must be entirely controlled.
By interfacing its ADJ pin with the OUTPUT ensures that the current at the OUTPUT is continually checked by the ADJ terminal and is never permitted to go past the foreordained level set by the resistor.
The gadget can bolster no less than 3 amps of current through it, in this manner effortlessly gets to be good to drive 1 to 5 quantities of 1 watt LEDs, each having their own particular current constraining resistors.
The present limiting resistors can be tried different things with, presumably lesser values may be tried for increasing the luminosity levels of the LEDs, however anything under 50 Ohms ought not be attempted, in light of the fact that it may bring about a perpetual harm to the LEDs.
The data to the LM 338 IC can be from a directed DC control supply, fit for supplying 12 volts at 3 amps or more.
The IC LM 338 ought to be mounted over a heatsink for better execution.
The data diode ought to be appraised at 3 amps, so a 1N5408 turns out to be OK for the application.
In the event that the circuit is expected for working outside, the data may be taken from a 12 v battery, as from a vehicles battery.
For L = 3 Watt LED:
R = 1.8 Ohms of 2 Watt
For L = 5 Watt LED:
R = 1.05 Ohms of 4 Watt
Tuesday, 3 November 2015
Remote control switch on or off for home appliances
dvbot
11:24
BC548, BC558, Remote control switch on or off for home appliances, using IC CD4017
No comments
![]()
The 38kHz infrared (IR) beams produced by the remote control are received by IR collector module TSOP1738 of the circuit.
Pin 1 of TSOP1738 is associated with ground, pin 2 is joined with the power supply through resistor R5 and the output is taken from pin 3. The output signal is increased by transistor T1 (BC558).
The amplifier signal is given to clock pin 14 of decade counter IC CD4017 (IC1). Pin 8 of IC1 is grounded, pin 16 is joined with Vcc and pin 3 is associated with LED1 (red), which shines to demonstrate that the machine is "off."
The output of IC1 is taken from its pin 2. LED2 (green) associated with pin 2 is utilized to demonstrate the "on" condition of the apparatus. Transistor T2 (BC548) joined with pin 2 of IC1 drives hand-off RL1. Diode 1N4007 (D1) goes about as a freewheeling diode. The machine to be controlled is associated between the pole of the relay and neutral terminal of mains. It gets associated with live terminal of AC mains by means of normally opened (N/O) contact when the relay energizes.
Simple Car Audio Amplifier Circuit
dvbot
11:14
amplifier using TDA2003, car amplifier, simple auto amplifier
No comments
![]()
The circuit utilizes low cost, promptly accessible components and it is anything but difficult to develop.
TDA2003 is an integrated car radio amplifier from ST Micro electronics that has a ton of good elements like short circuit protection for all the pins, heat over range level low harmonic distortion, low traverse bending and so on.
In the circuit given here each TDA2003 is wired as a mono amplifier working from a 12V DC supply. Resistors R2 and R3 shapes a feedback system that sets the amplifier gain. C7 is the input DC de-coupling capacitor and C5 couples the speaker to the amplifiers yield. C4 is utilized for enhancing the swell dismissal or ripple rejection while C1 and C2 are utilized for power supply filteration. C3 and R1 are utilized for setting the upper frequency cut-off. Network containing C6 and R4 is utilized for frequency adjustment and to avoid oscillation.
Friday, 16 October 2015
Using Arduino as a simple Web Server along with Ethernet shield
dvbot
03:00
arduino mega and uno, arduino web server, atmega328, ethernet shield, simple web server
No comments
![]()
- Control hardware from the webpage like fan or lights (using Javascript buttons).
- Read the state of a switch which can be either ON or OFF (using simple HTML).
- Read value of a sensors connected to Arduino board (using simple HTML).
Arduino Board

Ethernet Shield

Hardware needed:
To use an Arduino Board as a Simple Web server, you need the following:
DC Voltage of 5V from Arduino - To power the Ethernet Shield
Ethernet shield - To connect with LAN
Connection speed: 10/100Mb - For optimum performance.
Connection with Arduino on SPI port
The Ethernet shield will connect the Arduino board to the Web or Internet. Setup is very simple, Just plug the header pins of the shield into your Arduino, then connect an Ethernet cable to the shield. In the figure below, you can see an Arduino Mega with an Ethernet shield installed and connected with internet.

Now let's get to the working.
We will demonstrate how to use the Arduino as a Web server, in the further experiment we will find how Arduino can show the state of a switch through sending information as a web server. Giving it's output in html pages
Components required:
- 1 x Ethernet cable
- 1 x Wi-Fi Router (Optional)
- 1 x Arduino Mega2560 or Arduino UNO
- 1 x Ethernet Shield
- 1 x Breadboard or blank circuit board can do as well
- 3 x Jumper Wires
- 1 x 1k Resistor
- 2 x 9VDC Adaptor
- 1 x Push button
Schematic
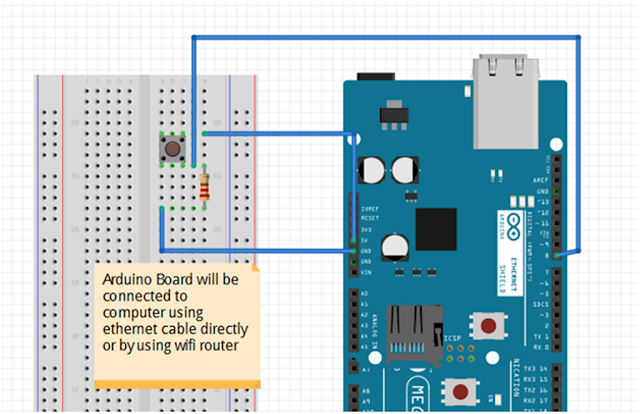
To control the Ethernet shield, you utilize the Ethernet.h library.
The shield must be allocated a MAC and IP address utilizing the Ethernet.begin() function. For a specific gadget, a MAC address is an all around extraordinary identifier. Current Ethernet shields accompany a sticker showing the MAC address. For more seasoned shields, an arbitrary one ought to work, however one should not utilize the same MAC address for many Ethernet Shields. Legitimacy of IP address relies on upon the arrangement of one's network. In the event that DHCP is utilized, it might dynamically assign an IP to the shield.
IP ADDRESS
IP address (Internet Protocol address) is a numerical name allotted to every gadget participating in a PC system that uses the Internet Protocol for correspondence. To indicate the IP address which is done inside the system. It is basic:
byte ip[] = { 192, 168, 0, 112 } and change it to match one own setup. For instance, if the switch's IP location is 192.168.0.60, and the scanner has 192.168.0.40, So I will allot the IP of Ethernet shield to 192.168.0.50 with the assistance of taking after order:
byte ip[] = { 192, 168, 0, 50 };
The initial three bytes ought to be same and it should not have similar IP address as any of other devices connect in same LAN.
MAC ADDRESS
MAC address (media access control location) is an exceptional identifier doled out to every gadget taking an interest in a physical system. Every bit of systems administration gear has an one of a kind serial number to recognize itself over a system and this is typical hard-modified into the hardware's firmware. In any case, with Arduino, we can characterize the MAC address our self.
byte mac[] = { 0x90, 0xA2, 0xDA, 0x0D, 0x85, 0xD9 };
You can set the subnet and portal with the assistance of taking after charges:
byte subnet[] = { 255, 255, 255, 0 }; /allocating subnet veil
byte gateway[] = { 192, 168, 0, 1 }; /allocating entryway
Along these lines, to setup Ethernet Shield, the square of code is given below:
/********************ETHERNET SETTINGS ********************/
byte mac[] = { 0x90, 0xA2, 0xDA, 0x0D, 0x85, 0xD9 }; /allotting MAC address
byte ip[] = { 192, 168, 0, 112 }; /ip in lan
byte subnet[] = { 255, 255, 255, 0 }; /allotting subnet mask
byte gateway[] = { 192, 168, 0, 1 }; /allotting default gateway
The following is a picture of the connection, demonstrating how the Arduino board unites with the Wi-Fi switch. The Ethernet link associate shield with the switch and switch then join remotely with the portable workstation. Or you can just connect the Ethernet shield directly to your home router or switch.

Program
Below is the script that outputs HTML of a simple Web page.
client.println("<!DOCTYPE html>"); //web page is made using HTML
client.println("<html>");
client.println("<head>");
client.println("<title>Ethernet Tutorial</title>");
client.println("<meta http-equiv=\"refresh\" content=\"1\">");
client.println("</head>");
client.println("<body>");
client.println("<h1>A Webserver Tutorial </h1>");
client.println("<h2>Observing State Of Switch</h2>");
client.print("<h2>Switch is: </2>");
if (digitalRead(8))
{
client.println("<h3>ON</h3>");
}
else
{
client.println("<h3>OFF</h3>");
}
client.println("</body>");
client.println("</html>");This program will display a web page on a Web browser when the IP address assigned to the Arduino is accessed.
The line:
client.println("<http-equiv=\"refresh\" content=\"1\">");Educates the browser to refresh the page. At the point when the page is accessed once again, the Arduino will again read the switch's status and present it in the output.
Recall that, you can simply see the source code of the displayed Web page. On pushing the push button, you can watch the changing condition of the switch in the webpage.
You can likewise set this up to keep running without the switch. To do this you have to:
- Assign a manual IP address to the Arduino's Ethernet say 192.168.0.2 and Subnet mask 255.255.255.0 default Gateway empty.
- Use a cross-over Ethernet cable to link the two (laptop and Arduino).
- We should then be able to get your Arduino site up on http://192.168.0.2 from the laptop.
#include <SPI.h>
#include <Ethernet.h>
/******************** ETHERNET SETTINGS ********************/
byte mac[] = { 0x90, 0xA2, 0xDA, 0x0D, 0x85, 0xD9 }; //physical mac address
byte ip[] = { 192, 168, 0, 112 }; // ip in lan
byte subnet[] = { 255, 255, 255, 0 }; //subnet mask
byte gateway[] = { 192, 168, 0, 1 }; // default gateway
EthernetServer server(80); //server port
void setup()
{
Ethernet.begin(mac,ip,gateway,subnet); // initialize Ethernet device
server.begin(); // start to listen for clients
pinMode(8, INPUT); // input pin for switch
}
void loop()
{
EthernetClient client = server.available(); // look for the client
// send a standard http response header
client.println("HTTP/1.1 200 OK");
client.println("Content-Type: text/html");
client.println("Connnection: close");
client.println();
/*
This portion is the webpage which will be
sent to client web browser one can use html , javascript
and another web markup language to make particular layout
*/
client.println("<!DOCTYPE html>"); //web page is made using html
client.println("<html>");
client.println("<head>");
client.println("<title>Ethernet Tutorial</title>");
client.println("<meta http-equiv=\"refresh\" content=\"1\">");
/*
The above line is used to refresh the page in every 1 second
This will be sent to the browser as the following HTML code:
<meta http-equiv="refresh" content="1">
content = 1 sec i.e assign time for refresh
*/
client.println("</head>");
client.println("<body>");
client.println("<h1>A Webserver Tutorial </h1>");
client.println("<h2>Observing State Of Switch</h2>");
client.print("<h2>Switch is: </2>");
if (digitalRead(8))
{
client.println("<h3>ON</h3>");
}
else
{
client.println("<h3>OFF</h3>");
}
client.println("</body>");
client.println("</html>");
delay(1); // giving time to receive the data
/*
The following line is important because it will stop the client
and look for the new connection in the next iteration i.e
EthernetClient client = server.available();
*/
client.stop();
} Hope you liked this project. For more projects related to Arduino or any other electronic please message me or write them in the comments. Thursday, 8 October 2015
Simple +-400Watt Amplifier using TDA7294 or TDA7293 + Power Transistors 2SC5200 and 2SA1943
dvbot
00:47
powerful amplifier using tda7293 and tda7294 using extra transistors 2sc5200 and 2sa1943, transistor and chip amp hybrid
No comments
![]()
The traditional chip amp produces about 40-50watt rms output which isn't any less but by adding these power transistors it can maximize the output to extreme.
This is the classic TDA7294 AMP with LOTS more Power then normal, this is with using Power Transistors at the output stage, it is a simple Addon to make, it just requires a SYNC resistor and the feedback to be moved to the output after the Power Transistors.
So to make this AMP you can just start with the TDA7294 with one change, just need to "move" the feedback so you can connect it to the Output after the Power Transistors, in all the AMPS that have been made with the TDA7294 the 6.8Ohm has been spot on when using the 2SC5200 & 2SA1943, if you use other transistors you may need to experiment with another value for the SYNC resistor.
Things to do when SYNC it is to listen to it, things to listen to are from very low volume (FROM a clean source) and go slowely up in volume, the POINT here is that it should just get louder like a normal amplifier would, if the SYNC is off then a normal thing will be that at audio peaks (like drums & bass) it will sound like someone is kicking your speakers because the Transistors kick in at a wrong volume then the amp is playing, believe me you will hear it, this needs to be corrected by changing the resistor else you will have an amp that only sounds good at very low volume and medium to high volume.
Component list: (1x AMP)
1x 680 (680R) Resistor
1x 10K Resistor
3x 22K Resistor
1x 6.8 (6R8) 5W Resistor
2x 0.15 (0R15) 5W Resistor
2x 10uF 50V Capacitor
2x 22uF 50V Capacitor
1x 1uF 63V MKT/BiPolar Capacitor
1x TDA7294 Chip AMP
1x 2SA1943 PNP Transistor
1x 2SC5200 NPN Transistor

Output Power: The output is at 400W+ (MAX) and this is based on that the TDA itself adds ONLY 20-40W (because of the much higher driving Ohm), but the 5200/1943 are some GOOD POWERFULL transistors and going through the datasheet it will deliver peeks over 600W (short pulse pr Transistor), they supply 100W but this is FULL DC and there are no audio tracks to my knowledge that has that kind of "sound"
Driving Impedance: We have been using it for 2-8Ohm speakers, the lowest we have driven was 1.3Ohm but as with all AMPS if you know your Transistors you know how many watts you can pull out, this AMP will drive what ever you hook it up to, JUST one thing, when we were using my 1.3Ohm set it did introduce some "noise" (sounded like 80' AMP hiss), and at this point the SYNC resistor properly needs to be changed, we did not do this, we took the lazy way out and put some 1.8Ohm POWER Resistors in line with the speakers instead.
We have been using this AMP for +3 years, it is good for driving 2-8Ohm speakers with current config (6.8Ohm RES & 5200/1943)














